The new way of modeling the Earth’s climate
Bogdan Góralski
Library of the History Faculty of the University of Warsaw.
Abstract
Since 2013 I have conducted continuous observations of LOD and Poland’s weather changes, and today I can say that LOD changes we can use for modeling weather and climate modeling. The IERS provides data on Earth orientation, on the International Celestial Reference System/Frame, on the International Terrestrial Reference System/Frame, and the half-year forecasts of LOD changes. Based on this forecast, we can model climate changes on Earth using my climate change model. I observed the negative correlation of atmospheric pressure at SLP sea level (in Reykjavik, Iceland) and a positive correlation SLP in Ponta Delgada (Azores)with changes in LOD (length of day). This correlation confirms the existence of a close dependence of terrestrial climate changes on LOD changes and the changes of gravitational pulling of the Earth by solar system objects. These impacts and their results are explained in my book ‘A modern look at the Earth’s climate mechanism and the cosmo-geophysical system of the Earth’ published in 2019 on the Internet (Google Books and Academia.edu). The following work and drawings contained in it are probably proof of the truthfulness of my theory of the Earth’s climate mechanism described in the above book.
Changes in LOD versus SLP changes in atmospheric pressure in Reykjavik in Iceland [hPa] during the period 1985-1988

Fig. 1. Changes in LOD (color orange right scale in [ms]) versus SLP changes in atmospheric pressure in Reykjavik in Iceland [hPa] during the period 1985-1988
Source of SLP in Reykjavik: Icelandic Met Office link: https://en.vedur.is/climatology/data/
Source of delta LOD values: Earth Orientation Center IERS
Changes in LOD versus SLP changes in atmospheric pressure in Reykjavik in Iceland [hPa] during the period 2015-2018
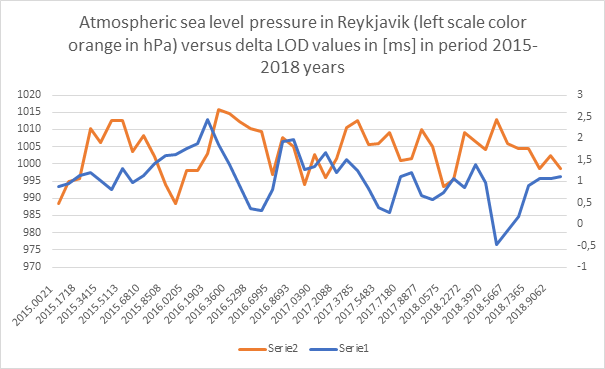
Fig.2 Changes in delta LOD (color orange right scale in [ms]) versus SLP changes in atmospheric pressure in Reykjavik in Iceland [hPa] during the period 2015-2018
Source of SLP in Reykjavik: Icelandic Met Office link: https://en.vedur.is/climatology/data/
Source of delta LOD values: Earth Orientation Center IERS
We see on Fif.1 and Fig.2 the negative correlation of both series of data SLP in Reykjavik and delta LOD.
Correlation of atmospheric pressure changes in Ponta Delgada in Azores and delta LOD (length of day) changes in periods 1985-1988

Fig.3 Changes in delta LOD (color orange right scale in [ms]) versus SLP changes in atmospheric pressure in Ponta Delgada in the Azores [hPa] during period 1985-1988
Source of data SLP in Ponta Delgada 1985-1988
https://psl.noaa.gov/gcos_wgsp/Timeseries/NAO_AZO/
Source of delta LOD values: Earth Orientation Center IERS
We see postive correlation of both sereies of data SLP in Ponta Delgada and delta LOD.
The LOD data (on the above plots) was subjected to Lagrange interpolation with an interpolation period of 31 days.
Comparison of SLP in Ponta Delgada and SLP in Reykjavik in period January 1985-December 1988.

Fig. 4 Comparison of SLP in Ponta Delgada (blue one) and SLP [in hPa] in Reykjavik in period January 1985-December 1988.
We see the negative correlation of both series of data SLP in Ponta Delgada and Reykjavik.
Conclusions
In Fig.1, 2, we see a negative correlation between SLP and LOD, i.e., a decrease in the Earth’s rotational speed (increase in delta LOD value) causes a reduction in atmospheric pressure in Reykjavik and vice versa.
In Fig.3, we see a positive correlation between SLP and delta LOD, i.e., a decrease in the Earth’s rotational speed (increase in delta LOD value) causes an increase in atmospheric pressure in Ponta Delgada and vice versa.
In.Fig 4 we see the negative correlation of SLP in Reykjavik and Ponta Delgada.
My nineteen years of research on the Earth’s climate mechanism can be used to the general forecast climate and weather changes in Europe and Poland. Further work on my climate theory will probably allow for accurate global climate and weather forecasts.
Warsaw, 23 March 2021, 5:20 Bogdan Góralski

